一天一点学习Linux之硬盘的分区与格式化
发布时间:2014-09-05 16:46:40作者:知识屋
引言
为什么要把硬盘分区?
1、维护相关:如可以把相同类型,有共同安全需要的内容,放到不同的分区中,这样方便了维护。
2、效率因素:如果一个大的硬盘,在整个硬盘上找到相应的资料,很费时。
3、硬盘限额:限额的控制,只能对分区来实施。
4、备份资料:这个和第一个控制有一点雷同,我可以对重要的信息放到某个分区,方便备份。
5、安全考虑:如果大的硬盘,一但有损坏的话,就有可能导致整个硬盘资料丢失,如果把硬盘的资料分开来存放的话,损失会很小。
你可以把这个磁盘想像成您家的房子,而分区就相当于房子里面的房间一样。
为什么要对分区进行格式化?
格式化就是对分区进行初始化的一种操作,为了让我们能向分区中写入数据。如果你看过一天一点学习Linux之认识文件系统 的话,那么就你会明白格式化操作其实就是创建分区的Inode/block/super block/group block等等信息。
第一部分:磁盘的分区
下面我们就用虚拟机来实验RHEL6上的硬盘分区与格式化
在虚拟机上增加一块硬盘
我以VMware workstation为例,演示如何给RHEL6系统上增加一块SCSI硬盘,并设置大小写为20G。
关机状态下:在VMware Workstation的工具栏中选择VM——Settings——Hardware——Add——选择Hard Disk——Next——Create a virtual disk——Next——SCSI(Recommended)——Next——Maximum disk size(GB):20.0——Next——Finish
这样就就为你的系统增加了一块20G的SCSI的硬盘了,然后启动系统,下面就开始今天的分区操作了。
对硬盘进行分区操作
[root@yufei ~]# fdisk -l
显示出系统中所有的硬盘信息
[root@yufei ~]# fdisk -l
Disk /dev/sda: 21.5 GB, 21474836480 bytes
255 heads, 63 sectors/track, 2610 cylinders
Units = cylinders of 16065 * 512 = 8225280 bytes
Sector size (logical/physical): 512 bytes / 512 bytes
I/O size (minimum/optimal): 512 bytes / 512 bytes
Disk identifier: 0x00093fdc
#设备名 是否是启动设备 开始柱面 结果柱面 大小1K为单位 分区类型标识 分区的系统类型
Device Boot Start End Blocks Id System
/dev/sda1 * 1 1913 15360000 83 Linux
/dev/sda2 1913 1978 524288 82 Linux swap / Solaris
Disk /dev/sdb: 21.5 GB, 21474836480 bytes #磁盘的名称、大小
255 heads, 63 sectors/track, 2610 cylinders #磁头、扇区、柱面数量
Units = cylinders of 16065 * 512 = 8225280 bytes#每个柱面的大小
Sector size (logical/physical): 512 bytes / 512 bytes#扇区的大小
I/O size (minimum/optimal): 512 bytes / 512 bytes #硬盘的IO情况
Disk identifier: 0x00000000 ##磁盘的标识
Disk /dev/sdb doesn't contain a valid partition table
这里面会显示磁盘的空间大小以及磁头、扇区、柱面的数量。如果没有分区的磁盘,他会给有相应的提示“Disk /dev/sdb doesn’t contain a valid partition table”。这就是我们要对其分区的磁盘sdb。
[root@yufei ~]# fdisk /dev/sdb
显示fdisk的帮助信息
Command (m for help):m #显示帮助信息
Command action
a toggle a bootable flag
b edit bsd disklabel
c toggle the dos compatibility flag
d delete a partition #删除一个分区
l list known partition types #列出分区类型
m print this menu
n add a new partition #增加一个新的分区
o create a new empty DOS partition table
p print the partition table #打印出分区表
q quit without saving changes #不保存退出
s create a new empty Sun disklabel
t change a partition's system id #改变分区类型
u change display/entry units
v verify the partition table #校验分区表
w write table to disk and exit #保存分区表
x extra functionality (experts only)
新增分区
Command (m for help): n
Command action
e extended #扩展分区
p primary partition (1-4) #主分区
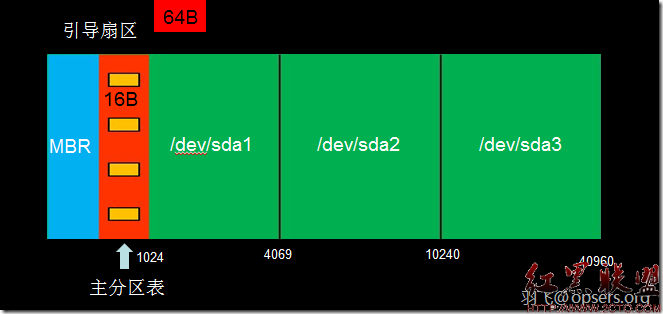
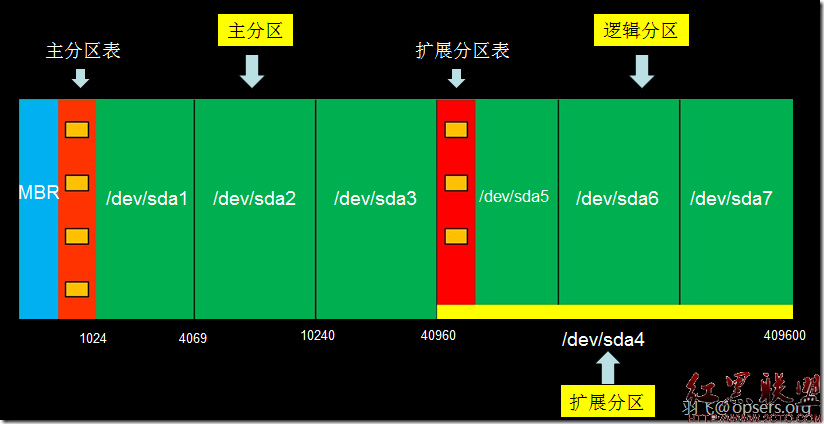
由于硬盘的设计原因,我们的主分区表最多是4个。至于为什么会是这样,请大家参考:带您深入了解硬盘分区表http://www.opsers.org/base/take-you-in-depth-understanding-of-the-hard-disk-partition-table.html。如果想更详细了解的话,请观看我以前的视频内容:Linux分区与格式化及文件系统优化http://www.opsers.org/videos/chapter-x-linux-partition-and-format-and-file-system-optimization.html
p
Partition number (1-4): 1 #分区号
First cylinder (1-2610, default 1): #柱面默认是1,直接回车
Using default value 1
Last cylinder, +cylinders or +size{K,M,G} (1-2610, default 2610):+1G #设置结束柱面或者用分区的大小(+K、M、G)来让系统自动计算结束柱面 然后回车
列出分区信息
Command (m for help): p #列出刚才的分区信息
Disk /dev/sdb: 21.5 GB, 21474836480 bytes
255 heads, 63 sectors/track, 2610 cylinders
Units = cylinders of 16065 * 512 = 8225280 bytes
Sector size (logical/physical): 512 bytes / 512 bytes
I/O size (minimum/optimal): 512 bytes / 512 bytes
Disk identifier: 0xd6737273
Device Boot Start End Blocks Id System
/dev/sdb1 1 132 1060258+ 83 Linux
Command (m for help): n
Command action
e extended
p primary partition (1-4)
p
Partition number (1-4): 2
First cylinder (133-2610, default 133):
Using default value 133
Last cylinder, +cylinders or +size{K,M,G} (133-2610, default 2610): +50 #在原来的基础上加上50个柱面
Command (m for help): p
Disk /dev/sdb: 21.5 GB, 21474836480 bytes
255 heads, 63 sectors/track, 2610 cylinders
Units = cylinders of 16065 * 512 = 8225280 bytes
Sector size (logical/physical): 512 bytes / 512 bytes
I/O size (minimum/optimal): 512 bytes / 512 bytes
Disk identifier: 0xd6737273
Device Boot Start End Blocks Id System
/dev/sdb1 1 132 1060258+ 83 Linux
/dev/sdb2 133 183 409657+ 83 Linux
新增加扩展分区
Command (m for help): n
Command action
e extended
p primary partition (1-4)
e #我们来分扩展分区
Partition number (1-4): 3 #扩展分区的分区号是3,当然也可以是4,但不可能是大于4的。
First cylinder (184-2610, default 184): #扩展分区的起始柱面
Using default value 184
Last cylinder, +cylinders or +size{K,M,G} (184-2610, default 2610): #扩展分区的结束柱面,默认就是全部划分给扩展分区了
Using default value 2610
Command (m for help): p
Disk /dev/sdb: 21.5 GB, 21474836480 bytes
255 heads, 63 sectors/track, 2610 cylinders
Units = cylinders of 16065 * 512 = 8225280 bytes
Sector size (logical/physical): 512 bytes / 512 bytes
I/O size (minimum/optimal): 512 bytes / 512 bytes
Disk identifier: 0xd6737273
Device Boot Start End Blocks Id System
/dev/sdb1 1 132 1060258+ 83 Linux
/dev/sdb2 133 183 409657+ 83 Linux
/dev/sdb3 184 2610 19494877+ 5 Extended #注意这里的类型已经和上面的不一样了
增加逻辑分区
Command (m for help): n
Command action
l logical (5 or over) #这时候就和上面的不一样了,因为在扩展分区中再分的话,就是逻辑分区了,必需是5以上
p primary partition (1-4) #因为我们还可以分一个主分区出来,所以这里会显示这样的信息。当然,因为我们已经把硬盘所有我空间全分给了扩展分区,所以,我们分不出那个主分区了。
l
First cylinder (184-2610, default 184):
Using default value 184
Last cylinder, +cylinders or +size{K,M,G} (184-2610, default 2610): +2G
Command (m for help): P
Disk /dev/sdb: 21.5 GB, 21474836480 bytes
255 heads, 63 sectors/track, 2610 cylinders
Units = cylinders of 16065 * 512 = 8225280 bytes
Sector size (logical/physical): 512 bytes / 512 bytes
I/O size (minimum/optimal): 512 bytes / 512 bytes
Disk identifier: 0xd6737273
Device Boot Start End Blocks Id System
/dev/sdb1 1 132 1060258+ 83 Linux
/dev/sdb2 133 183 409657+ 83 Linux
/dev/sdb3 184 2610 19494877+ 5 Extended
/dev/sdb5 184 445 2104483+ 83 Linux #这个分区就是逻辑分区了,我是怎么看出来的呢?关键是你要注意两点:1是分区号。这里是sdb5。2是分区的开始柱面是从184开始的,而我们的扩展分区也是从184开始的,可以肯定是在扩展分区里面分出来的分区,那当然是逻辑分区啊
增加SWAP分区
下面我们再分一个512M的分区出来,为了我们后面的课程讲解。这个分区我们后面会用他当作SWAP分区。
Command (m for help): n
Command action
l logical (5 or over)
p primary partition (1-4)
l
First cylinder (446-2610, default 446):
Using default value 446
Last cylinder, +cylinders or +size{K,M,G} (446-2610, default 2610): +512M
Command (m for help): p
Disk /dev/sdb: 21.5 GB, 21474836480 bytes
255 heads, 63 sectors/track, 2610 cylinders
Units = cylinders of 16065 * 512 = 8225280 bytes
Sector size (logical/physical): 512 bytes / 512 bytes
I/O size (minimum/optimal): 512 bytes / 512 bytes
Disk identifier: 0xd6737273
Device Boot Start End Blocks Id System
/dev/sdb1 1 132 1060258+ 83 Linux
/dev/sdb2 133 183 409657+ 83 Linux
/dev/sdb3 184 2610 19494877+ 5 Extended
/dev/sdb5 184 445 2104483+ 83 Linux
/dev/sdb6 446 511 530113+ 83 Linux
我们下面来个错误的演示
Command (m for help): n
Command action
l logical (5 or over)
p primary partition (1-4)
p
Selected partition 4
No free sectors available
因为已经没有剩余的扇区了,所以肯定是分不了主分区了。
转换分区类型
Command (m for help): l #这个是L的小写,不是1啊!就是列出分区的类型,因为很多,所以我就找几个出来
82 Linux swap / #这个就是SWAP分区代码了
83 Linux #这个就是Linux系统的分区代码了
8e Linux LVM #LVM分区的代码
Command (m for help): t #转换分区类型
Partition number (1-6): 6 #选择转换的分区号
Hex code (type L to list codes): 82 #转换成的类型
Changed system type of partition 6 to 82 (Linux swap / Solaris) #提示内容
Command (m for help): p
Disk /dev/sdb: 21.5 GB, 21474836480 bytes
255 heads, 63 sectors/track, 2610 cylinders
Units = cylinders of 16065 * 512 = 8225280 bytes
Sector size (logical/physical): 512 bytes / 512 bytes
I/O size (minimum/optimal): 512 bytes / 512 bytes
Disk identifier: 0xd6737273
Device Boot Start End Blocks Id System
/dev/sdb1 1 132 1060258+ 83 Linux
/dev/sdb2 133 183 409657+ 83 Linux
/dev/sdb3 184 2610 19494877+ 5 Extended
/dev/sdb5 184 445 2104483+ 83 Linux
/dev/sdb6 446 511 530113+ 82 Linux swap / Solaris
我们就先分这么多出来,当然这个磁盘还有很多空间,因为这只是演示,所以无需全部来分完。下面就是重要一个环节,保存我们分好的分区表,如果不保存,那么我们刚才的功劳,等于没有做。
保存分区表
Command (m for help): w #保存分区表
The partition table has been altered!
Calling ioctl() to re-read partition table.
Syncing disks.
注意,如果出现
The kernel still uses the old table.
The new table will be used at the next reboot.
这样的提示的话,他的意思就是让我们重新启动系统,好让内核认出我们新的分区表,为了不让系统重新启动,我们可以用
partprobe
这个命令,来让内核重新获得一次分区表的信息。
这时候我们再用
[root@yufei ~]# fdisk -l
就可以看到我们分出来的分区内容了,我只取有用的内容
Disk /dev/sdb: 21.5 GB, 21474836480 bytes
255 heads, 63 sectors/track, 2610 cylinders
Units = cylinders of 16065 * 512 = 8225280 bytes
Sector size (logical/physical): 512 bytes / 512 bytes
I/O size (minimum/optimal): 512 bytes / 512 bytes
Disk identifier: 0xd6737273
Device Boot Start End Blocks Id System
/dev/sdb1 1 132 1060258+ 83 Linux
/dev/sdb2 133 183 409657+ 83 Linux
/dev/sdb3 184 2610 19494877+ 5 Extended
/dev/sdb5 184 445 2104483+ 83 Linux
/dev/sdb6 446 511 530113+ 82 Linux swap / Solaris
如果说,你在分区的时候,哪里出现了错误,或者是不想那么操作的话,按q退出,然后重新来过即可。千万在确保正确后再用w保存哦,如果你分错了硬盘的话,那么数据就OVER了!!
这个分区其实很简单,关键是多操作几次,熟练后就很容易了!
注意:SATA 硬盘最多能够支持到15个分区,IDE 则可以支持到63个。如果超过了这个限制,那么你的硬盘多余的空间也就浪费。
第二部分:格式化
分区完,我们的这块硬盘还是不能使用的,需要对分区进行格式化,让其变成系统认识的分区。关于格式化的原理,大家可以参考:Linux分区与格式化及文件系统优化这里我就不多说了,下面进行格式化的操作。
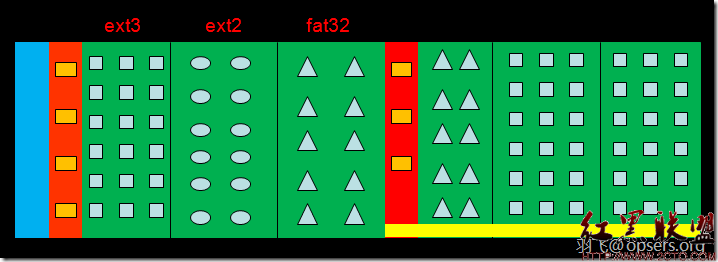 下面我们以第一个分区为列来讲解如何对分区进行格式化
下面我们以第一个分区为列来讲解如何对分区进行格式化
先查看我们要进行格式化的磁盘分区情况
[root@yufei ~]# fdisk -l /dev/sdb
Disk /dev/sdb: 21.5 GB, 21474836480 bytes
255 heads, 63 sectors/track, 2610 cylinders
Units = cylinders of 16065 * 512 = 8225280 bytes
Sector size (logical/physical): 512 bytes / 512 bytes
I/O size (minimum/optimal): 512 bytes / 512 bytes
Disk identifier: 0xd6737273
Device Boot Start End Blocks Id System
/dev/sdb1 1 132 1060258+ 83 Linux
/dev/sdb2 133 183 409657+ 83 Linux
/dev/sdb3 184 2610 19494877+ 5 Extended
/dev/sdb5 184 445 2104483+ 83 Linux
/dev/sdb6 446 511 530113+ 82 Linux swap / Solaris
再来认识一下格式化的工具
mkfs [-t 文件系统格式] 设备名
或者是
mkfs.文件系统格式 设备名
用mkfs[tab][tab]就可以显示出系统所有支持的格式了
这个里面有很多的参数,可以用–hlep来查看
[root@yufei ~]# mkfs.ext4 --hlep
mkfs.ext4: invalid option -- '-'
Usage: mkfs.ext4 [-c|-l filename] [-b block-size] [-f fragment-size]
[-i bytes-per-inode] [-I inode-size] [-J journal-options]
[-G meta group size] [-N number-of-inodes]
[-m reserved-blocks-percentage] [-o creator-os]
[-g blocks-per-group] [-L volume-label] [-M last-mounted-directory]
[-O feature[,...]] [-r fs-revision] [-E extended-option[,...]]
[-T fs-type] [-U UUID] [-jnqvFKSV] device [blocks-count]
-b 指定block的大小1024 2048 4096 默认是4096
-I 指定inode的大小(min 128/max 4096) 默认是256
-i 指定多少个字节分配一个inode
-L 指定卷标
分区演示
[root@yufei ~]# mkfs.ext4 -L opsers_tech -b 2048 -i 10240 /dev/sdb1
mke2fs 1.41.12 (17-May-2010)
Filesystem label=opsers_tech
OS type: Linux
Block size=2048 (log=1)
Fragment size=2048 (log=1)
Stride=0 blocks, Stripe width=0 blocks
106128 inodes, 530128 blocks
26506 blocks (5.00%) reserved for the super user
First data block=0
Maximum filesystem blocks=537919488
33 block groups
16384 blocks per group, 16384 fragments per group
3216 inodes per group
Superblock backups stored on blocks:
16384, 49152, 81920, 114688, 147456, 409600, 442368
Writing inode tables: done
Creating journal (16384 blocks): done
Writing superblocks and filesystem accounting information: done
This filesystem will be automatically checked every 32 mounts or
180 days, whichever comes first. Use tune2fs -c or -i to override.
因为我的分区很小,所以格式化是很快的,如果分区很大的话,这个也是要消耗一些时间的。大家可以用默认格式化与自定义格式化来进行对比。
希望大家和其他三篇文章结合起来看,我相信这三篇文章,应该能彻底的让你了解并掌握磁盘的分区、格式化原理与优化了。
一天一点学习Linux之认识文件系统:
一天一点学习Linux之文件系统属性更改相关操作:
Linux分区与格式化及文件系统优化:
注意:如果你遇到了这样的提示
/dev/sdx:No such file or directory //找不到该分区,无法格式化
那么和我们上面的是一样的原因,就是内核无法读到新的分区表。解决方法有两个
1.重启系统。系统重新启动的时候会重新加载分区表,新的分区自然也就生效了。
2.为了节省时间或者系统环境不允许重启,使用partprobe命令,在不重启情况下重新加载分区表。
[root@yufei ~]# partprobe //重新加载所有硬盘的分区表
[root@yufei ~]# partprobe /dev/sdb //只重新加载第一块硬盘的分区表
如果没有那个命令的话,那就安装
rpm -q parted
相关知识
-
linux一键安装web环境全攻略 在linux系统中怎么一键安装web环境方法
-

Linux网络基本网络配置方法介绍 如何配置Linux系统的网络方法
-
Linux下DNS服务器搭建详解 Linux下搭建DNS服务器和配置文件
-
对Linux进行详细的性能监控的方法 Linux 系统性能监控命令详解
-
linux系统root密码忘了怎么办 linux忘记root密码后找回密码的方法
-
Linux基本命令有哪些 Linux系统常用操作命令有哪些
-
Linux必学的网络操作命令 linux网络操作相关命令汇总
-
linux系统从入侵到提权的详细过程 linux入侵提权服务器方法技巧
-
linux系统怎么用命令切换用户登录 Linux切换用户的命令是什么
-
在linux中添加普通新用户登录 如何在Linux中添加一个新的用户
软件推荐
更多 >-
1
 专为国人订制!Linux Deepin新版发布
专为国人订制!Linux Deepin新版发布2012-07-10
-
2
CentOS 6.3安装(详细图解教程)
-
3
Linux怎么查看网卡驱动?Linux下查看网卡的驱动程序
-
4
centos修改主机名命令
-
5
Ubuntu或UbuntuKyKin14.04Unity桌面风格与Gnome桌面风格的切换
-
6
FEDORA 17中设置TIGERVNC远程访问
-
7
StartOS 5.0相关介绍,新型的Linux系统!
-
8
解决vSphere Client登录linux版vCenter失败
-
9
LINUX最新提权 Exploits Linux Kernel <= 2.6.37
-
10
nginx在网站中的7层转发功能